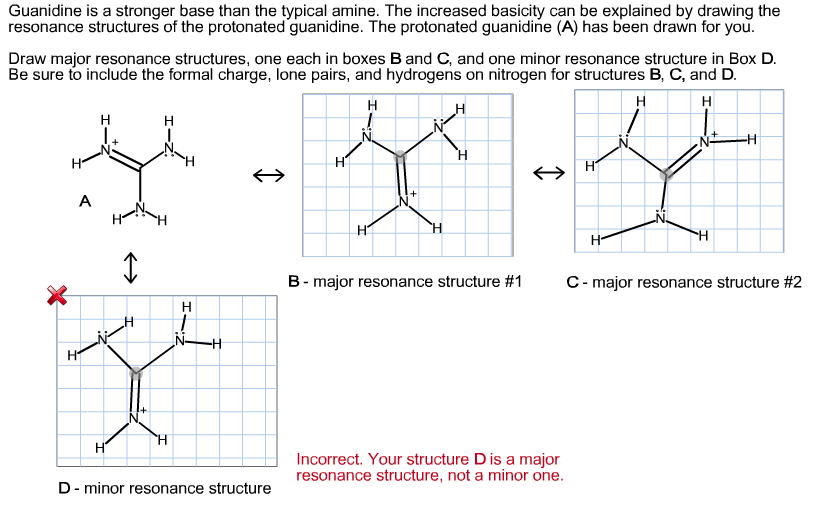
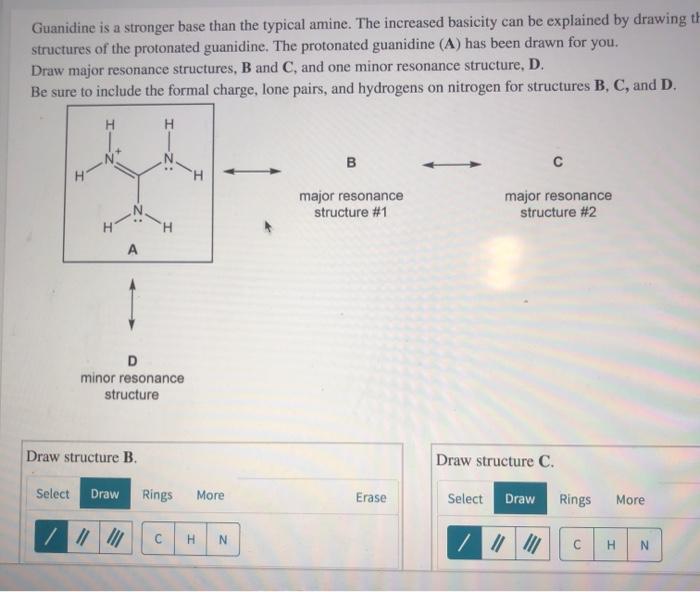
Using resonance theory,explain why guanidine is one of the strongest organic bases 11ea9a02_1c02_0d6d_8bb6_1347d1fc0690_TB5901_00Guanidine, CH 5 N 3, is de geconjugeerde base van guanidinium op dezelfde wijze als ammoniak de geconjugeerde base van het ammoniumion isGuanidine is een zeer sterke base, waarvan de sterkte in water niet accuraat bepaald kan worden De basesterkte wordt veroorzaakt door de mogelijkheid de positieve lading over de drie stikstofatomen te verdelenAre all the resonance structures of guanidine major contributors?
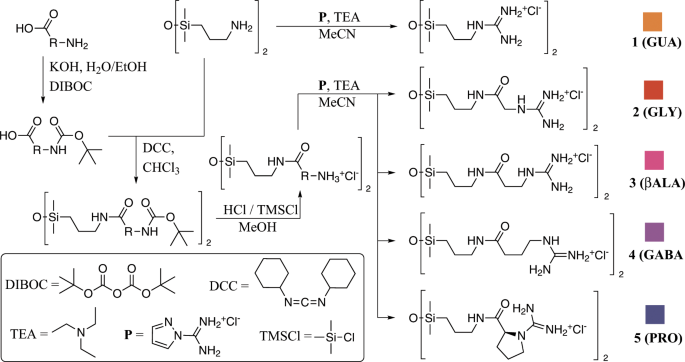
Exploring Ion Ion Preferences Through Structure Property Correlations Amino Acid Derived Bis Guanidinium Disiloxane Salts Scientific Reports
Guanidine resonance stabilization
Guanidine resonance stabilization-Guanine C5H5N5O CID structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safetyAnd simple ring systems in which the extended‐guanidine group is incorporated (3‐amino‐1,2,4‐triazole, 2,4‐diaminopyrimidine)


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com
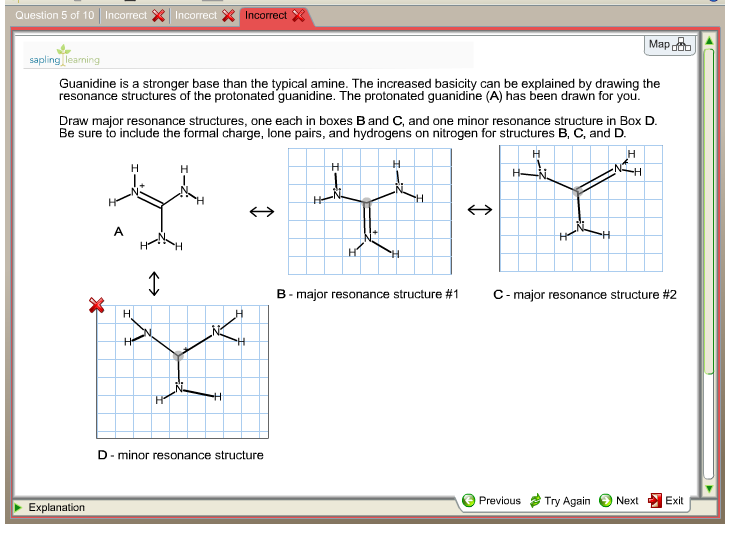
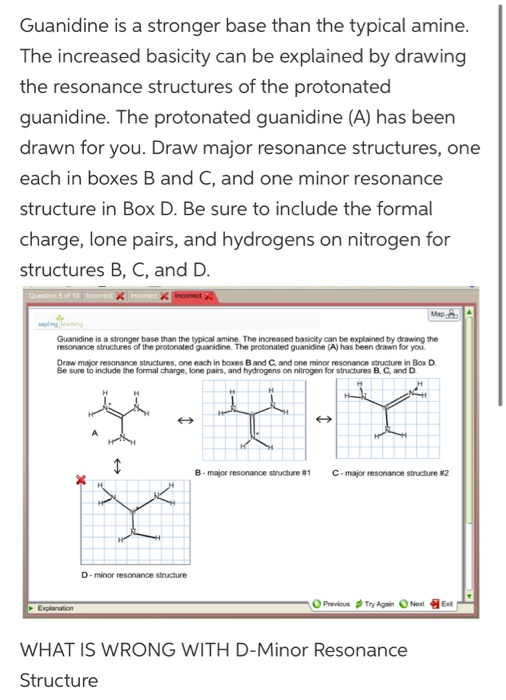
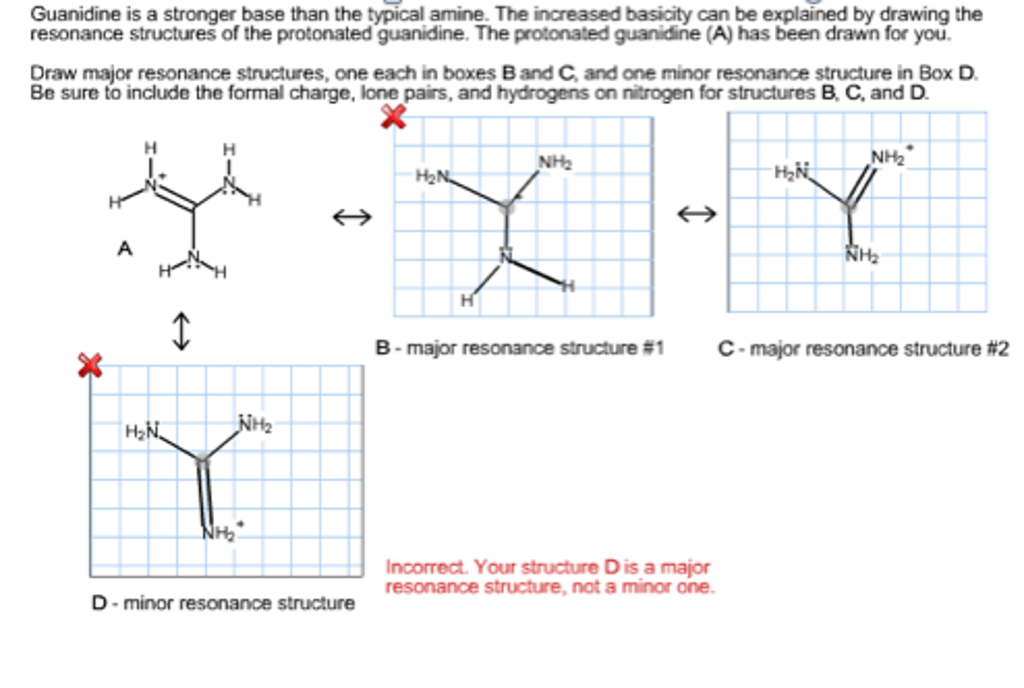
See the answer Guanidine is a stronger base than the typical amine The increased basicity can be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the protonated guanidine The protonated guanidine (A) has been drawn for you0421 · @article{osti_, title = {A comparative study on the aggregating effects of guanidine thiocyanate, guanidine hydrochloride and urea on lysozyme aggregation}, author = {Emadi, Saeed and Behzadi, Maliheh}, abstractNote = {Highlights • Lysozyme aggregated in guanidine thiocyanate (10 and M) • Lysozyme aggregated in guanidine hydrochloride (4The increased basicity can be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the protonated guanidine The protonated guanidine (A) has been drawn for you Draw major resonance structures, one each in boxes B and C, and one minor resonance structure in Box D Be sure to include the formal charge, lone pairs, and hydrogens on nitrogen for structures B, C, and D
This free chemistry help video tutorial shows you how to create and understand resonance structures for the acetate ionThe nuclear quadrupole resonance of nitrogen14 in guanidine monohydrochloride, guanidine acetate, guanidine oxalate, guanidine monothiocyanate, guanidine sulfate, guanidine carbonate, cyanoguanidine, ethylurea and symdiethylurea were observed at various temperatures · Guanidine Acetate, C(NHZ)3CH3C00 Four resonance frequencies were observed at 77 K and at 295 K Our frequency values agree closely with those determined by Oja (7);
Abstract An unusual type of π‐electron delocalization in Y‐shaped molecules related to guanidine and its protonated form, the guanidinium ion, has been studied by ab initio methods at the STO ‐3G and 3‐21G levels Results are reported for tautomeric, rotameric, and protonated forms of the oxygen‐substituted guanidine series (urea, carbamic, andThe guanidine and biguanidineporphyrins are poorly soluble in water, forming Jtype aggregates in aqueous solutions On the other hand, the porphyrinMLS peptide conjugate bearing a low molecular weight PEG spacer is highly watersoluble and does not aggregate in aqueous mediaGuanidine thiocyanate is used as a part of a lysis buffer solution which isolates and extracts the viral RNA from a sample This allows for relatively quick diagnosis of the virus in a subject It is so effective in fact that guanidine thiocyanate is becoming increasingly indemand and


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com


Diaminosquarate Bioisostere For The Guanidine Moiety As A Novel Hiv 1 Download Scientific Diagram
The 1 H resonances of the guanidine substituents indicate that both methyl and phenyl protons are shielded by the aromatic porphyrin group implying that these groups are poised on top of the porphyrin ring This ought to make the environment ofYou could say the diamide resonance is enhancedPure guanidine crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Pbca (no 61) and a = (2) Å, b = (2) Å, c = (4) Å at 100 K, Z = 16, with two Yshaped molecules in the asymmetric unit The compound features a threedimensional network of classical N–H···N hydrogen bonds Here, we present the results of a singlecrystal neutron diffraction study, performed at two



Amines The Organic Bases Categorizing Amines N Amines



Protonation Of Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange
· A new guanidine derivative named plantagoguanidinic acid was isolated from the seeds of Plantago asiatica The structure was elucidated by twodimensional (2D) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectral and other spectral methodsDistinct Effects of Guanidine Thiocyanate on the Structure of Superfolder GFP Olesya V Stepanenko1, Olga V Stepanenko1, Irina M Kuznetsova1, Daria M Shcherbakova2, Vladislav V Verkhusha2, Konstantin K Turoverov1* 1Laboratory of Structural Dynamics, Stability and Folding of Proteins, Institute of Cytology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, St Petersburg, Russia, · The presence of this force was evidenced by changes in the (1)H NMR and IR spectra before and after micelle formation of the guanidinetype (Gtype) surfactant, indicating that the increased assembly formability is caused by an increase in hydrogen bonding between guanidine groups of the surfactant via water molecules PMID



Epb1 Methods For The Synthesis Of Polycyclic Guanidine Compounds Google Patents


A Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely
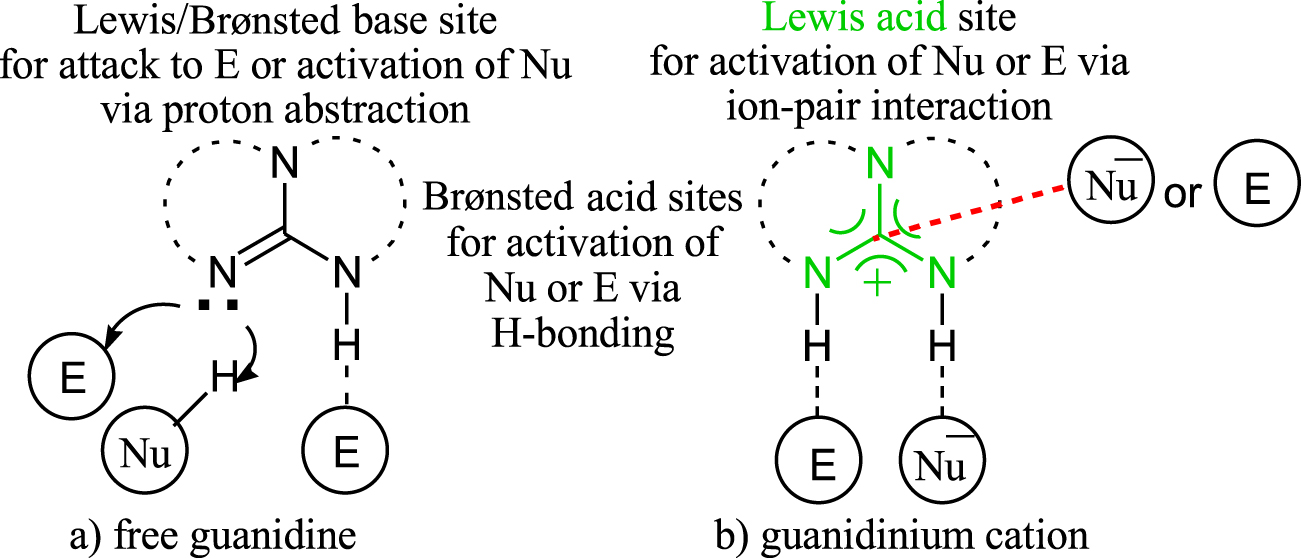
Explain pls 0 comments share save hide report 100% Upvoted Log in or sign up to leave a comment Log In Sign Up Sort by best no comments yet Be the first to share what you think!Synthesis and Coordination of a Neutral Phosphaguanidine and Comparison of its Basicity with a Guanidine January 21;Resonance Effects in Nitrogen Basicity The resonance effect also explains why a nitrogen atom is basic when it is in an amine, but not significantly basic when it is part of an amide group While the lone pair of electrons in an amine nitrogen is localized in one place, the lone pair on an amide nitrogen is delocalized by resonance



Which Is The Strongest Organic Nitrogen Base Quora



Vive 119 Guanidine Is Among The Strongest Neutral Base Nh Hnnh Guanidine The Reason For The
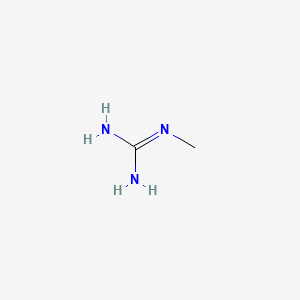
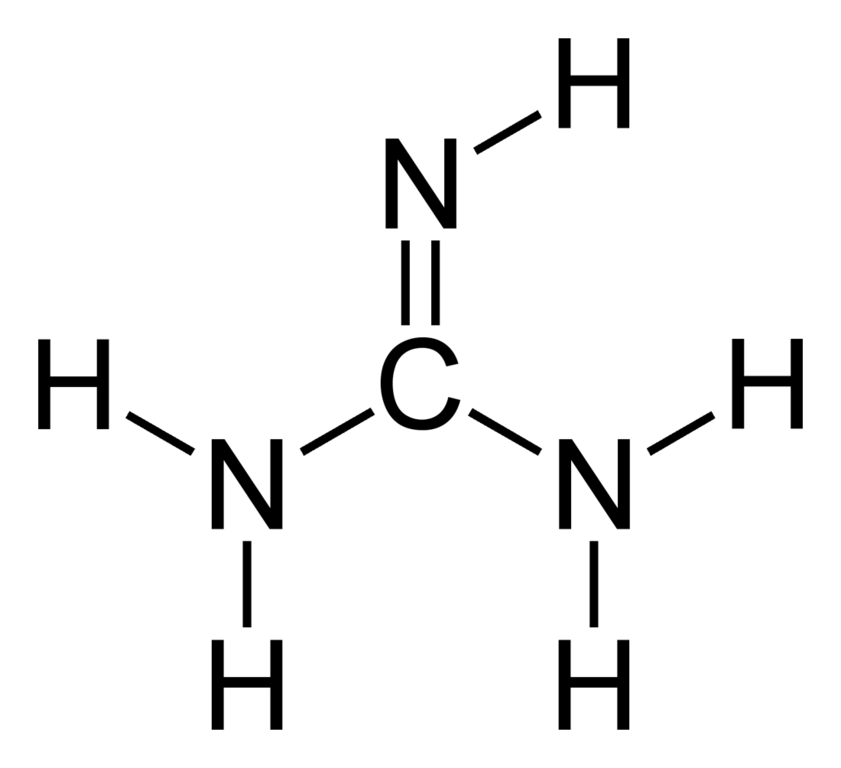
Guanidine is the compound with the formula HNC(NH2)2 121 relationsGuanidinium is a guanidinium ion It is a conjugate acid of a guanidine and a carbamimidoylazanium A strong organic base existing primarily as guanidium ions at physiological pH It is found in the urine as a normal product of protein metabolism It is also used in laboratory research as a protein denaturantNatural guanidines are a class of secondary metabolites characterized by the presence of the guanidine functionality, which is of limited occurrence in nature in natural products other than peptides produced by nonribosomal peptide synthetases or ribosomes, 1–10 since many peptides contain arginine in their structures
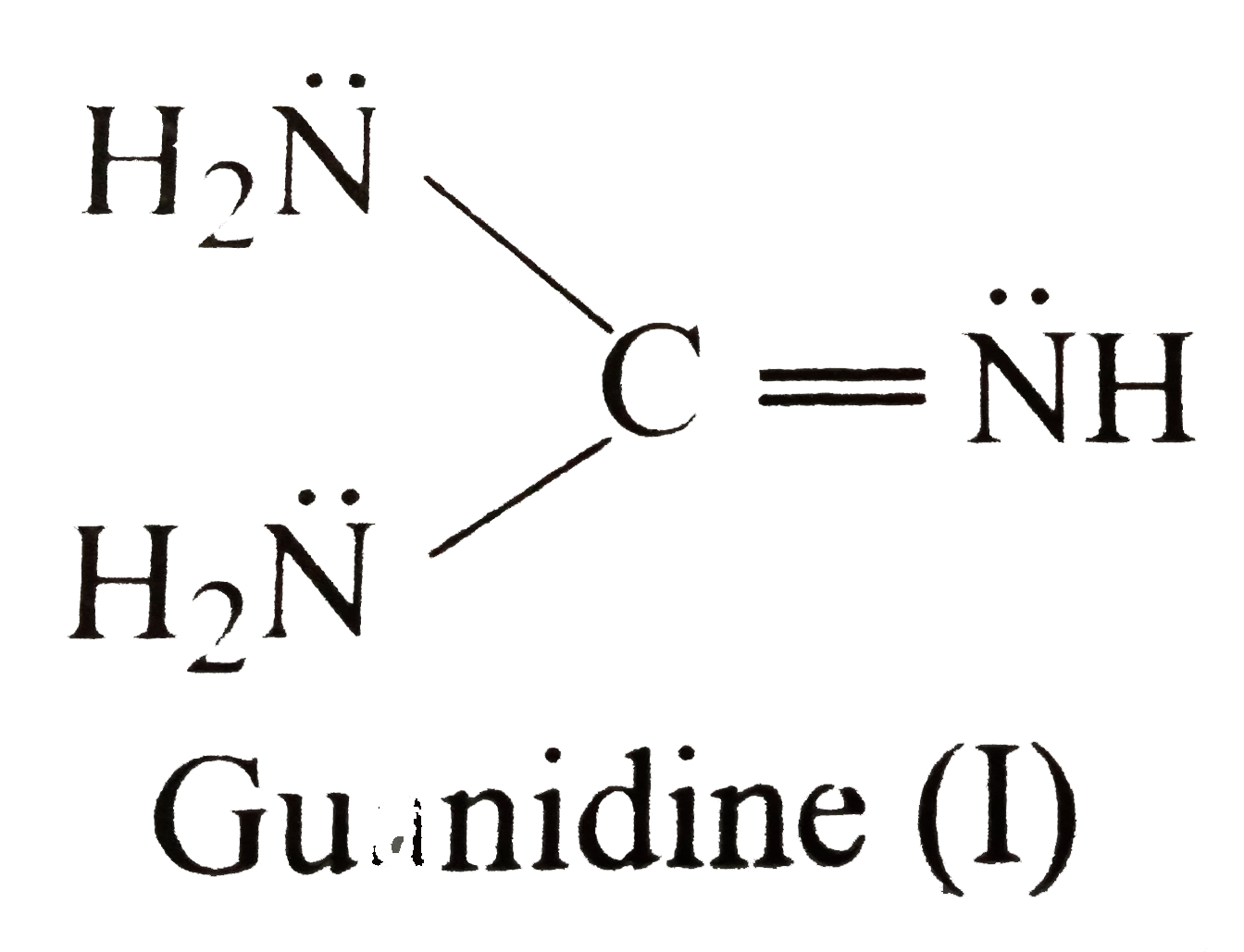


A Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely



Investigation On The Reaction Between Polyhexamethylene Guanidine Hydrochloride Oligomer And Glycidyl Methacrylate Wei 13 Journal Of Applied Polymer Science Wiley Online Library
· Resonance structures of guanidine I have learned about the octet rule, and I saw in some examples that it is however possible for a Catom to only have 6 electrons around him (like in pyridin ) So when i tried to calculate the Resonace structures of guanidine, I wondered why there must be 8 electrons around C this time (like this video )2106 · Solution for Draw the resonance forms of a protonated guanidino group, and explain why argininehas such a strongly basic isoelectric pointStructure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for Guanidine,


Chiral Organobases Properties And Applications In Asymmetric Catalysis



Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com
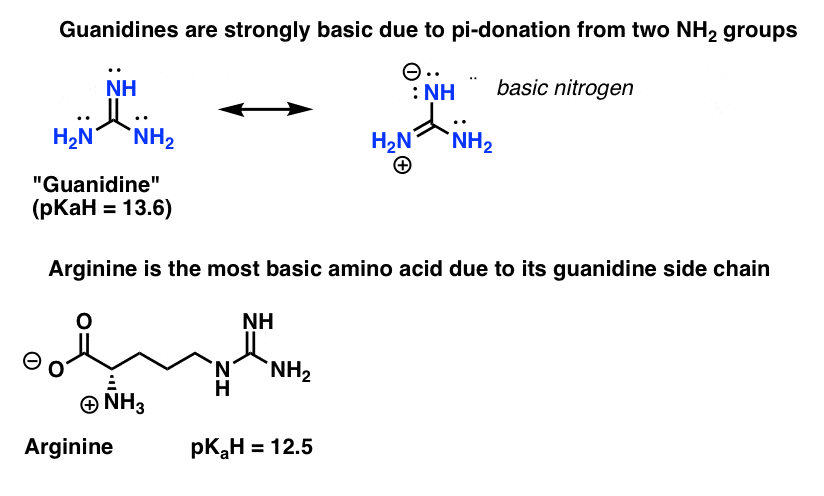
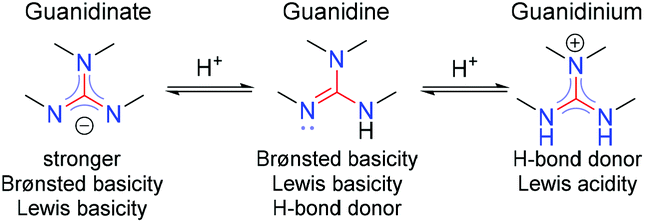
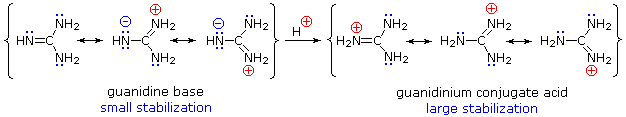
"extended‐guanidine" (aminomethylene guanidine) including pseudocyclic forms;Due to the resonance effect of the guanidine moiety 16,39 The compositional formula of the obtained white solids was confirmed by elemental analysis This result predicted that the zwitterionic adduct 2 and the bicarbonate salt 3 were prepared selectively under dry and wet conditions, respectively (Figure€1)Although resonance delocalization generally reduces the basicity of amines, a dramatic example of the reverse effect is found in the compound guanidine (pK a = 136) Here, as shown below, resonance stabilization of the base is small, due to charge separation, while the conjugate acid is stabilized strongly by charge delocalization


1 1 3 3 Tetramethylguanidine C5h13n3 Pubchem


Chemical Forums Resonance And Basicity
2 pts Guanidine is an exceptionally strong amine base Explain, providing the resonance structures of the conjugate acid q The conjugate acid of guanidine has 3 equivalent resonance structures, along with one other canonical structure, and is therefore rather highly resonanceGuanidine is isolobal to urea, where the carbonyl oxygen has been replaced by an imine $\ce{NH}$ However, in principle it is still the same flat, resonancestabilised molecule The main difference is that there is no 'preferred' site for the double bond — it could point towards any of the three nitrogens in theory; · Guanidine is a stronger base than the other two molecules shown because the guanidinium, the conjugate acid of guanidine, has a lot of resonance stabilization However, if the unprotonated molecule has a lot of resonance stabilization, and protonation produces a less resonance stabilized product, you will have a weaker base



Guanidine Formula Uses Facts Britannica
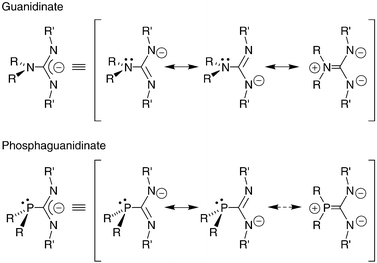


Lithium And Aluminium Complexes Supported By Chelating Phosphaguanidinates Dalton Transactions Rsc Publishing
It is a highly stable 1 cation in aqueous solution due to the efficient resonance stabilization of the charge and efficient solvation by water molecules As a result, its pK a is 136 8 meaning that guanidine is a very strong base in water;Canadian Journal of Chemistry 99(2) DOI /cjc0441 · adshelpatcfaharvardedu The ADS is operated by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory under NASA Cooperative Agreement NNX16AC86A



Epb1 Methods For The Synthesis Of Polycyclic Guanidine Compounds Google Patents
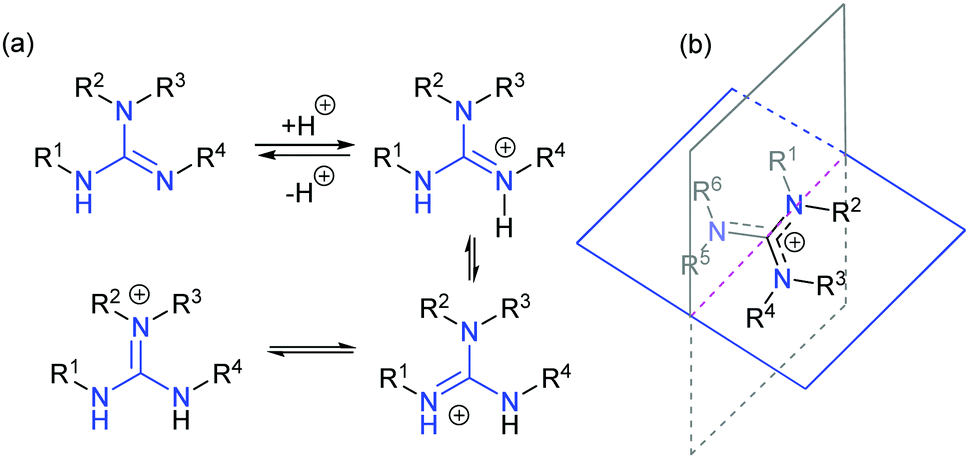


Chiral Guanidines And Their Derivatives In Asymmetric Synthesis Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C7csb
Results are reported for tautomeric, rotameric, and protonated forms of the oxygen‐substituted guanidine series (urea, carbamic, and carbonic acids);Guanidine hydrochloride, PharmaGrade, Manufactured under appropriate controls for use as a raw material in pharma or biopharmaceutical production, Guanidine hydrochloride, BioUltra, for molecular biology, ≥995% (AT),In neutral water, it



Synthesis And Coordination Of A Neutral Phosphaguanidine And Comparison Of Its Basicity With A Guanidine



Radiolabeled 4 Fluoro 3 Iodobenzyl Guanidine Improves Imaging And Targeted Radionuclide Therapy Of Norepinephrine Transporter Expressing Tumors Journal Of Nuclear Medicine
Read "Guanidinium‐Type resonance stabilization and its biological implications 2 The doubly‐extended‐guanidine series, Journal of Computational Chemistry" on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available atConformational changes at the active site of pantetheine hydrolase (EC351) during guanidine hydrochloride (GndHCl) denaturation were investigated by UV and circular dichroism spectroscopy and by electron spin resonance spectroscopy, following the spectral behaviour of the nitroxide radicals (N (1 oxyl 2,2,5,5, tetramethyl3pyrrolidinyl) iodacetamide) covalently linked to theView Entire Discussion (0 Comments)



Why There Is A Huge Difference Between The Basicity Of Urea And Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange



14n Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance Study Of Polymorphism In Famotidine Journal Of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Guanidine, acetate Copyright Copyright © 09 John Wiley & Sons, Inc All Rights Reserved Formula C3H9N3O2 InChI InChI=1S/C2H4O2CH5N3/c12(3)4;21(3)4/h1H3,(H,3,4);(H5,2,3,4) InChIKey DXTIKTAIYCJTIIUHFFFAOYSAN Instrument Name Varian A60 Sadtler NMR Number M Solvent D2O SpectraBase Batch ID DjlRigsOv7KA covalent rearrangement of the polypeptide bond at Asn(45)Gly(46) and/or Asn(51)Gly(52) that eventually yield βaspartic acids via deamidation of asparagine was observed to precede fibril formation Mutation of these asparagines to alanines resulted in delayed nucleus formationSitu resonance Raman investigations show that the rate determining step (rds) is O 2 binding to ferrous guanidine ligand, analogous to the active site of peroxidases, is determined to be very effective in enabling a facile and selective 4e /4H ORR Introduction



Molecules Free Full Text Guanidine Amide Catalyzed Aza Henry Reaction Of Isatin Derived Ketimines Origin Of Selectivity And New Catalyst Design Html



Acid Base Chemistry Of Organic Molecules Basicmedical Key
To test whether nanozymes exhibit an inactivation effect similar to that of natural enzymes, we used guanidine chloride (GuHCl) to disturb the iron oxide nanozyme (IONzyme) and observed that GuHCl induced IONzyme aggregation and that the peroxidaselike activity of IONzyme significantly decreased in the presence of GuHClHowever, contrary to Oja, we observed the low frequency pair to have about twice the intensity of the high frequency pairAn unusual type of π‐electron delocalization in Y‐shaped molecules related to guanidine and its protonated form, the guanidinium ion, has been studied



Guanidine Alchetron The Free Social Encyclopedia


Methylguanidine C2h7n3 Pubchem
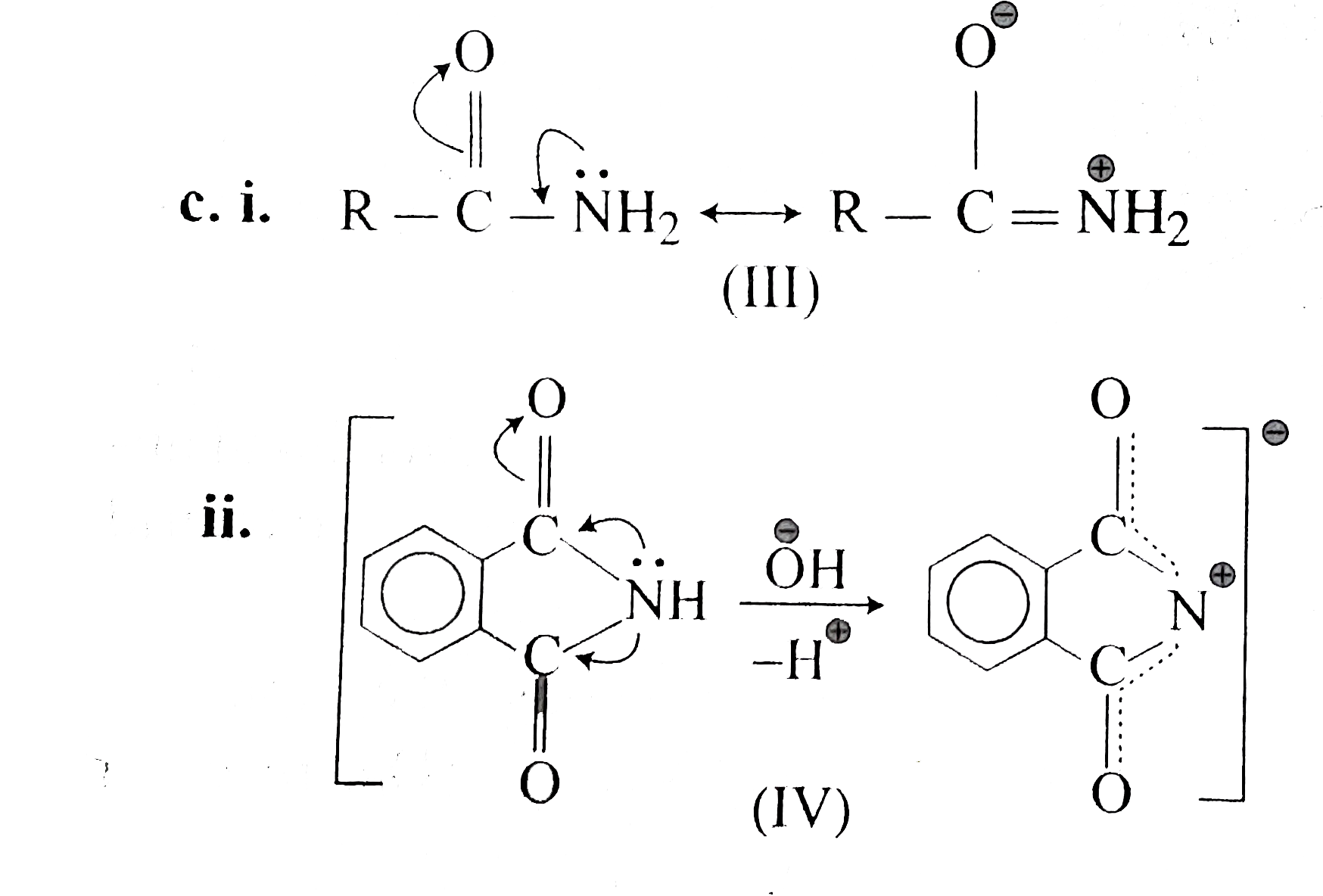
Guanidine is the compound with the formula HNC(NH 2) 2It is a colourless solid that dissolves in polar solvents It is a strong base that is used in the production of plastics and explosivesIt is found in urine as a normal product of protein metabolismA guanidine moiety also appears in larger organic molecules, including on the side chain of arginineMost resonance hybrids are not symmetric, however, and their contributors do not play equal roles Formamide is a superposition of III and IV, but its structure and properties more closely resemble III the atoms carry only small charges, the CO bond is closer to a double bond, and the CN bond is closer to a single bond



Why Are Amidines So Much More Basic Than Amides Chemistry Stack Exchange



The N Nitrosourea Of Szn Is Derived From An Intact Guanidine Group Of Download Scientific Diagram



With Aid Of Resonance Structures Show That Proton Transfer To Guanidine Occurs Preferentially To Its Nh B Than Its Nh 2 A Groups Study Com



Figure 1 From Non Covalent Interactions Complexes Of Guanidinium With Dna And Rna Nucleobases Semantic Scholar



Out Of The Given Compounds A And B The Number Of N Atoms In The Compound Which Is More Basic Are


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com



General Organic Chemistry 4 By Ankita Chowdhury Unacademy Plus



Protonation Of Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange


Guanidine Wikiwand



Which Nitrogen Is Prtonated Redily In The Guanidine


Exam 3 Answer Key



Molecules Free Full Text A Review On The Reactivity Of 1 Amino 2 Nitroguanidine Anq Html


Guanidine Metal Complexes For Bioinorganic Chemistry And Polymerisation Catalysis Springerlink


5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry
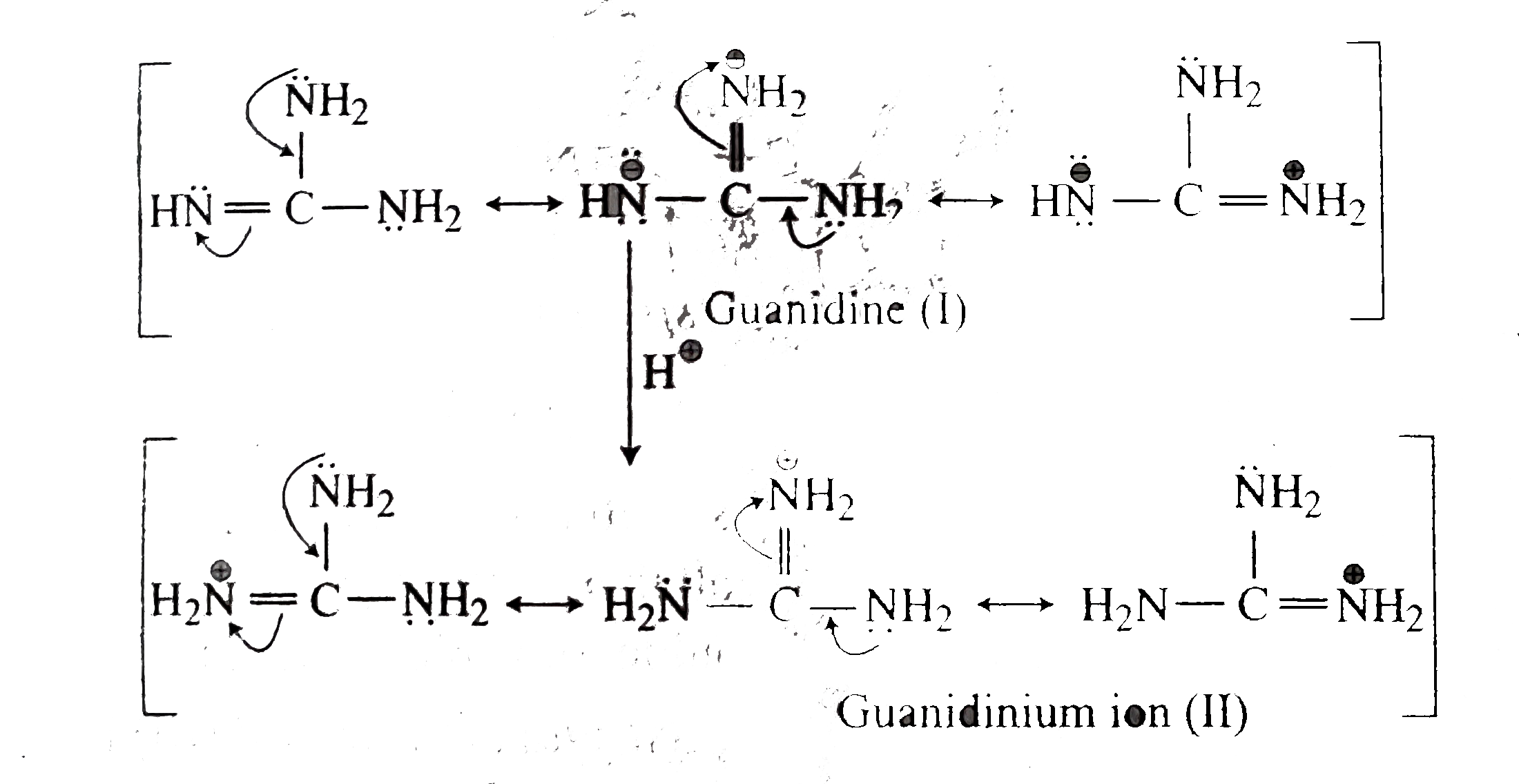


A Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely



With Aid Of Resonance Structures Show That Proton Transfer To Guanidine Occurs Preferentially To Its Nh B Than Its Nh 2 A Groups Study Com


Major And Minor Resonance Structures Organic Chemistry Socratic
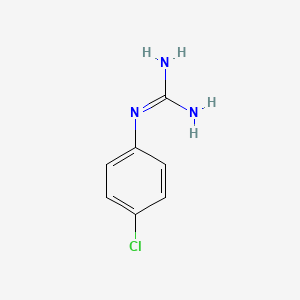


1 4 Chlorophenyl Guanidine C7h8cln3 Pubchem


Solved What Are The Resonance Structures And Which Is The Chegg Com
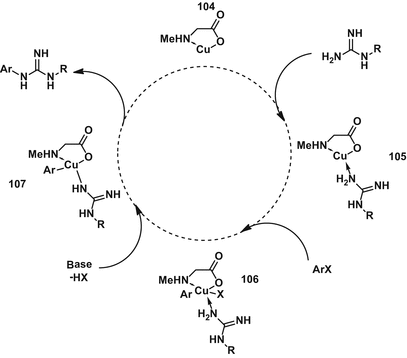


Synthesis Of Guanidines And Some Of Their Biological Applications Springerlink
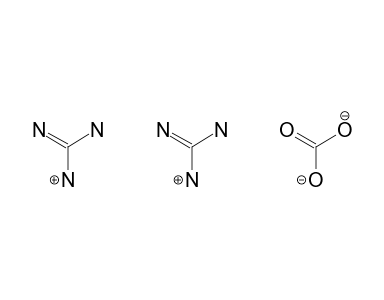


Guanidine Carbonate 13c Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase



Cleavage Of C N Bonds In Guanidine Derivatives And Its Relevance To Efficient C N Bonds Formation Sciencedirect
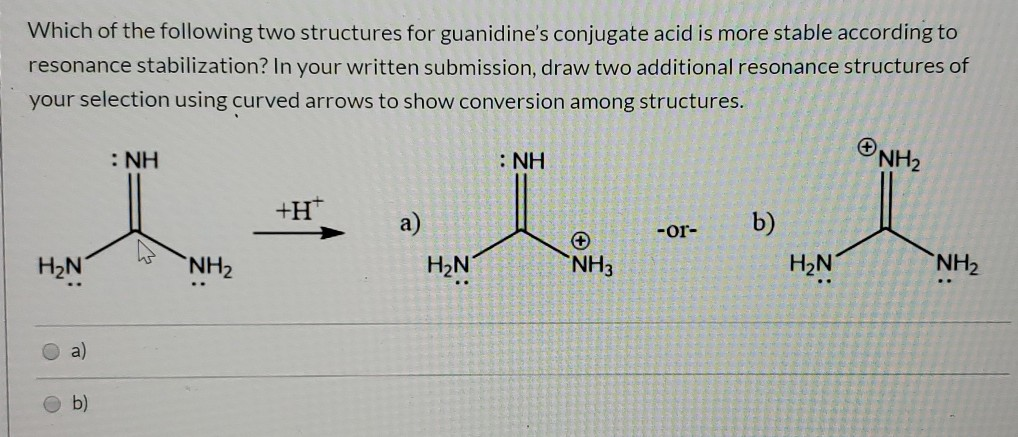


Solved Which Of The Following Two Structures For Guanidin Chegg Com


Solved Analyze The Two Compounds Below Circle The Structure Which Is Most Acidic Overall Discuss The Factors That Led You To This Choice Discus Course Hero
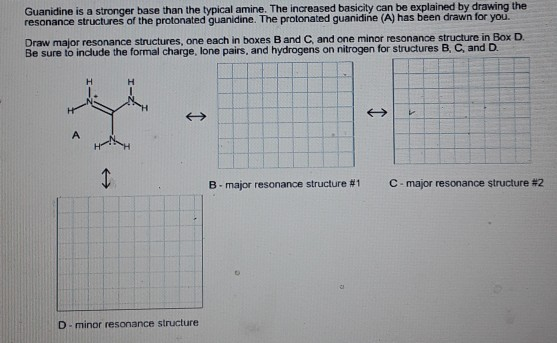


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com



Landolt Bornstein Substance Property Index


Which Is The Most Basic Nitrogen In Guanidine Quora



How To Solve These Problems 1 C Sony 2 Hani Nh2 One Has A Stronger Homeworklib


Metal Catalysed Reactions Enabled By Guanidine Type Ligands Organic Biomolecular Chemistry Rsc Publishing


Comptes Rendus Chimie



Of Two Possible Structures A And B For The Clutch Prep


File Guanidine 2d Png Wikipedia



Exploring Ion Ion Preferences Through Structure Property Correlations Amino Acid Derived Bis Guanidinium Disiloxane Salts Scientific Reports


Ch 610b


Py421 Week Two Review And Study Guide



Guanidine


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com


593 85 1 Guanidine Carbonate 075 Detail Information Laboratory Chemicals Fujifilm Wako Chemicals U S A Corporation



Organic Chemistry Video 17 Resonance Example 13 Guanidine Youtube


15 4 Basicity Of Amines Chemistry Libretexts


Ch 610b


Tautomer Wikipedia



Figure 1 4 From I The Synthesis And Coordination Chemistry Of Novel 6pi Electron Ligands Ii Improvement Of Student Writing Skills In General Chemistry Lab Reports Through The Use Of Calibrated Peer Review



Study Of The Carbon Dioxide Chemical Fixation Activation By Guanidines Sciencedirect



Unusual Oxidative Chemistry Ofn W Hydroxyarginine And N Hydroxyguanidine Catalyzed At An Engineered Cavity In A Heme Peroxidase Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Modified Guanidines As Chiral Auxiliaries Ishikawa 02 Chemistry A European Journal Wiley Online Library



Guanidines From Toxic Substances To Compounds With Multiple Biological Applications Detailed Outlook On Synthetic Procedures Employed For The Synthesis Of Guanidines Sciencedirect



Extensive In Vitro Activity Of Guanidine Hydrochloride Polymer Analogs Against Antibiotics Resistant Clinically Isolated Strains Sciencedirect



Synthesis And Coordination Of A Neutral Phosphaguanidine And Comparison Of Its Basicity With A Guanidine
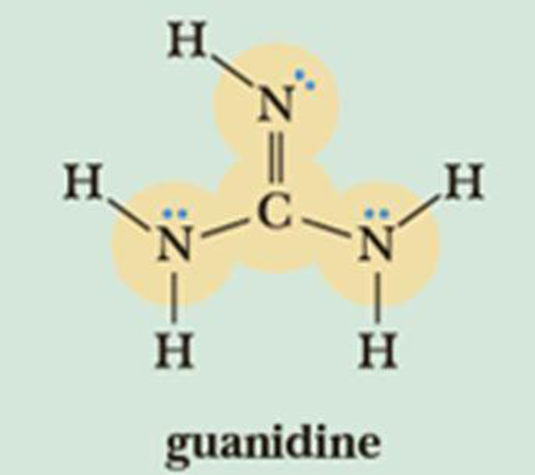


Draw Three Contributing Structures Of The Following Compound Called Guanidine And State The Hybridization Of The Four Highlighted Atoms In Which Orbitals Do The Three Lone Pairs Drawn Reside Bartleby



Figure 1 10 From Comparison Of Silica Based Poly Amine Containing Ion Exchangers And Their Guanidine Derivatives For Selective Pgm Recovery From Authentic Refinery Process Solutions Semantic Scholar
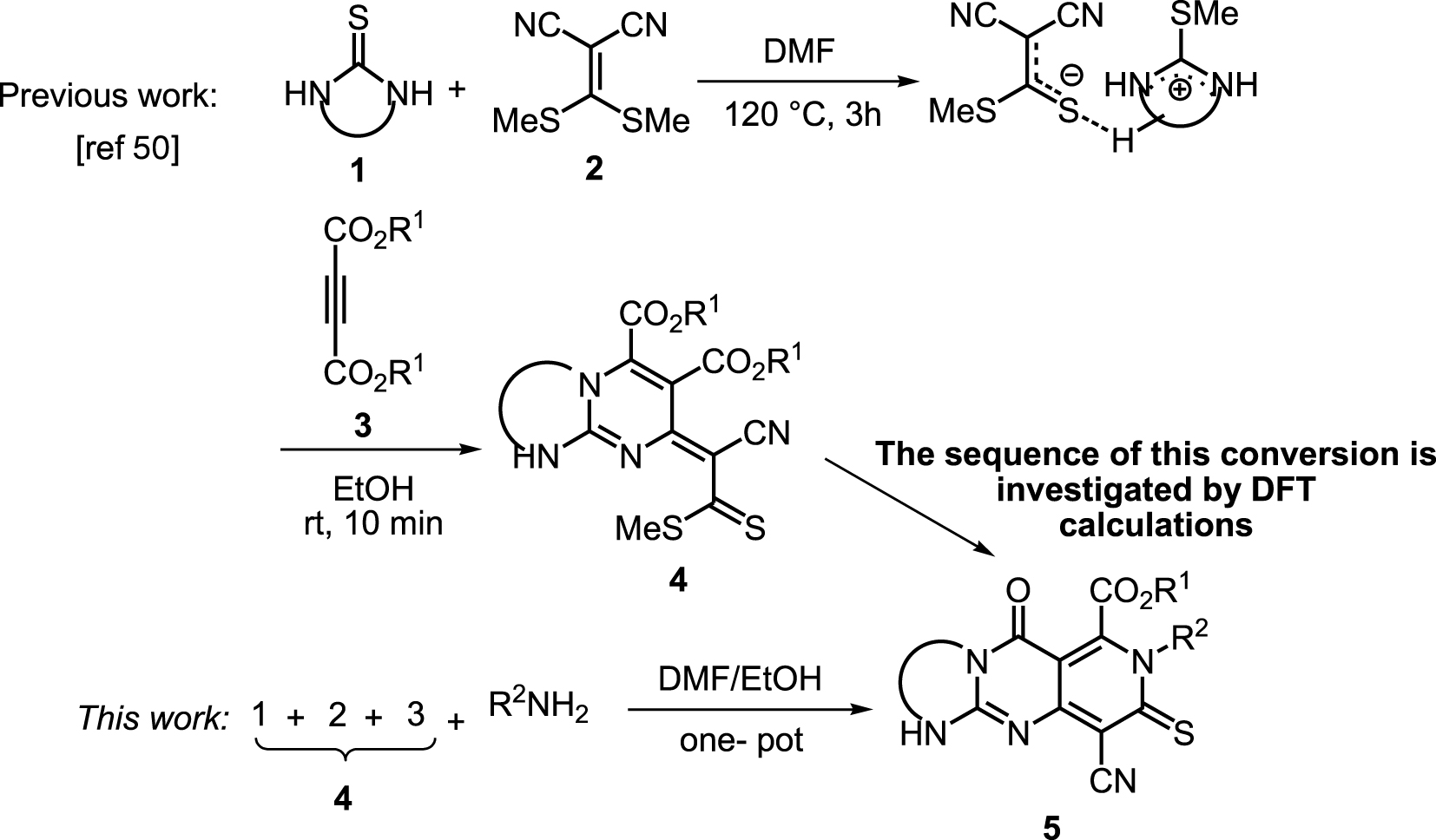


Comptes Rendus Chimie



Hindi General Organic Chemistry 2 By Prashant Soni Unacademy Plus



The 3rd One 3 Which Nitrogen Is Protonated Readily In The Guanidine Nha C 2 2 2 3 D Chemistry Alcohols Phenols And Ethers Meritnation Com



Cyclic Guanidine Compounds From Toxic Newts Support The Hypothesis That Tetrodotoxin Is Derived From A Monoterpene Kudo 16 Angewandte Chemie Wiley Online Library



Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine The Increased Basicity Can Be Explained By Brainly Com


Chiral Bicyclic Guanidine Bis Guanidinium Pentanidium And Related Organocatalysts Springerlink
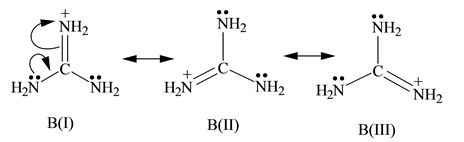


Solved Of Two Possible Structures A And B For The Conjugate Ac Chegg Com



Role Of Arginine Guanidinium Moiety In Nitric Oxide Synthase Mechanism Of Oxygen Activation Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Landolt Bornstein Substance Property Index
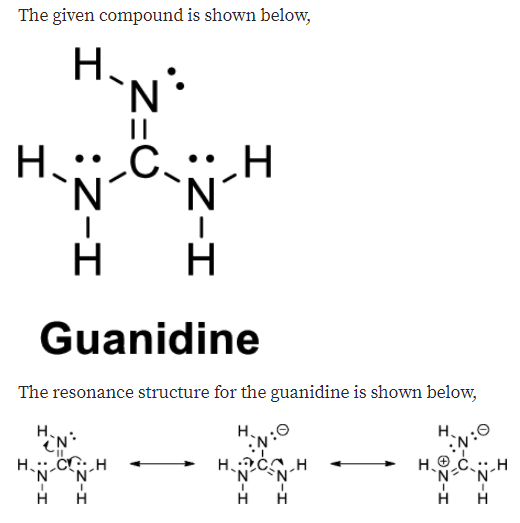


Answered Draw Three Contributing Structures Of Bartleby
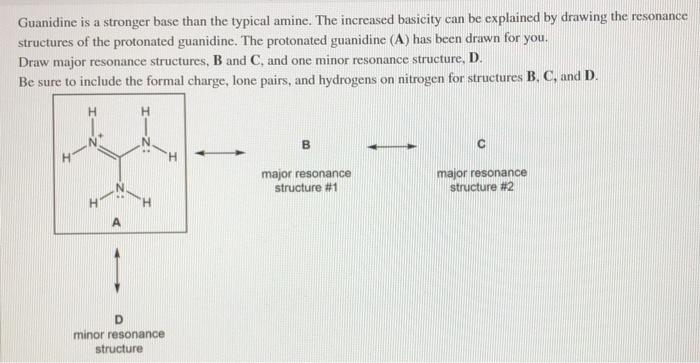


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com



Chemical Structure Of Three Amino Acids With Guanidinium Group Download Scientific Diagram



Why Is Guanidine More Basic Than Methylamine Student Doctor Network


Chemical Structure Of Three Amino Acids With Guanidinium Group Download Scientific Diagram


N 2 Benzimidazolyl Guanidine 1h Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase


Major And Minor Resonance Structures Organic Chemistry Socratic



Guanidine Hydrochloride
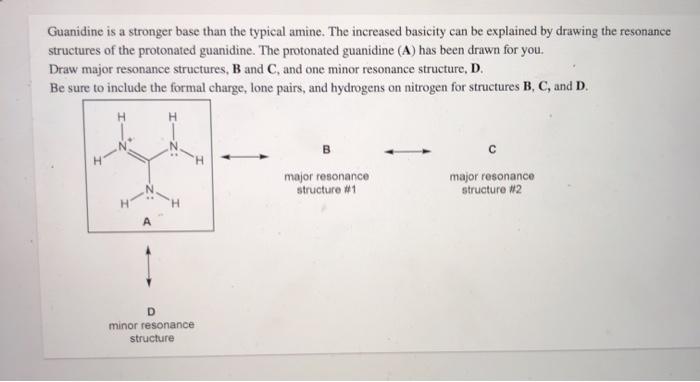


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com



Arginine Resonance Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Synthesis And Coordination Of A Neutral Phosphaguanidine And Comparison Of Its Basicity With A Guanidine



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿